Is your website struggling to rank despite your SEO efforts? You’re not alone. Many websites fail to reach their full potential simply because of overlooked on-page SEO issues. A well-executed on-page SEO audit can help you identify these roadblocks, leading to higher rankings, better visibility, and an improved user experience.
Regular SEO audits can boost organic traffic by as much as 61%, and optimized content found through these audits enjoys a 2.8 times higher click-through rate. But where do you start?
In this blog post, we’ll walk you through a free on-page SEO audit checklist, covering 10 essential steps to fix critical issues and enhance your website’s performance. Whether you’re looking for an on-page SEO audit for beginners or need a checklist for local SEO, this guide will help you take the right steps to optimize your site effectively.
Step #1: Check Your Organic Traffic
Before making any changes to your website, the first step in any on-page SEO audit checklist is to review your organic traffic. This gives you a clear picture of how your site is performing and helps you spot potential issues that could be hurting your rankings.
Use Google Analytics and Google Search Console to assess:
- Traffic trends: Is your organic traffic increasing, decreasing, or staying the same?
- Traffic drops: Identify any sudden declines and check if they align with Google algorithm updates.
- Top-performing pages: Find out which pages bring in the most organic visitors and what keywords they rank for.
- Mobile vs. desktop traffic: Ensure your website is performing well on all devices.
- Keyword ranking shifts: Look for any major ranking losses and analyze possible causes.
Open Google Search Console and go to Performance > Search Results. Check impressions, clicks, and CTR for key pages. Compare recent data with past performance to detect any significant drops. If you notice a decline, cross-check it with recent Google updates or content changes on your site.
A strong traffic analysis sets the foundation for the rest of your on-page SEO audit template. By identifying issues early, you can take targeted actions to improve rankings and increase organic traffic. Whether you’re following a free on-page SEO audit checklist or a checklist for local SEO, always start with data to guide your next steps.
Step #2: Run a Full Site Crawl
One of the most effective ways to uncover hidden SEO issues is by running a full site crawl. This process helps identify technical problems that may be preventing your pages from ranking well.
A site crawl will reveal:
- Broken links and redirect chains – 404 errors can harm user experience and SEO.
- Duplicate content and thin pages – Search engines may struggle to rank pages with similar or low-quality content.
- Orphan pages – Pages without internal links are harder for search engines to find and index.
- Indexing and crawlability issues – If search engines can’t properly crawl your site, important pages may not appear in search results.
To perform this step, use tools like Screaming Frog, Sitebulb, or Ahrefs. These tools will give you a detailed report on errors that need fixing.
- Fix broken links by redirecting or updating outdated URLs.
- Resolve duplicate content issues by consolidating similar pages or adding canonical tags.
- Ensure all important pages are internally linked to improve discoverability.
- Check your robots.txt file and meta tags to make sure search engines can index key pages.
A site crawl is a crucial part of any on-page SEO audit checklist, whether you’re working on a checklist for local SEO or optimizing a large website. By fixing these errors early, you ensure search engines can properly index and rank your pages, improving your overall search visibility.
Step #3: Improve Your On-Page SEO
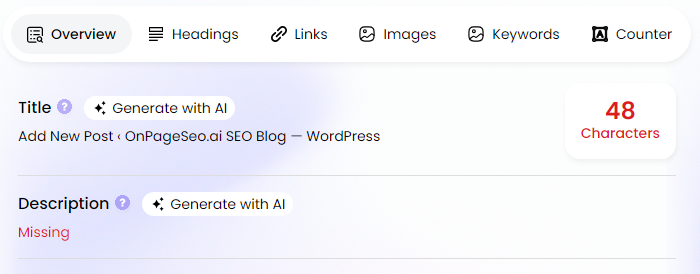
Search engines rely on on-page elements to understand your content and determine its relevance to search queries. At the same time, well-optimized pages can improve click-through rates (CTR), driving more organic traffic.
| Element | Common Issues | Optimization Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Title Tags & Meta Descriptions | Generic, vague, or keyword-stuffed titles and descriptions reduce CTR. Example: *”Best Shoes for Running | Make sure the tags and meta descriptions are relevant and made specifically for the content. |
| Header Tags (H1-H6) | Poor heading structure confuses users and search engines. Example: H1: “SEO Tips” → H2: “Things to Know” → H3: “More Info.” | Use a clear hierarchy to break down content logically. Example: H1: “On-Page SEO Checklist: 10 Steps to Optimize Your Website” → H2: “1. Conducting an On-Page SEO Audit for Beginners” → H3: “Why an On-Page SEO Audit Matters for Search Rankings.” |
| Keyword Optimization | Overusing the same keyword results in poor readability. Example: Repeating “on-page SEO checklist for website” excessively. | Use LSI (Latent Semantic Indexing) keywords like SEO audit checklist, on-page SEO audit template, how to do an on-page SEO audit to maintain natural readability. |
| Image Optimization | Large file sizes slow down the website, and missing alt text reduces accessibility. Example: Uploading “image123.png” without a description. | Compress images with TinyPNG and add descriptive alt text (e.g., “on-page-seo-checklist.png”). |
A well-optimized page is a critical component of any on-page SEO audit checklist. Whether you’re using a free on-page SEO audit checklist or a checklist for local SEO, refining these elements ensures better search visibility and higher engagement.
Use onpageSEO.ai to instantly analyze and optimize your title tags, meta descriptions, and header structure with AI-powered recommendations. Learn more about Optimizing Title Tags for Local SEO to boost local search visibility.
Step #4: Optimize for UX & Core Web Vitals
User experience (UX) plays a direct role in SEO rankings, and Google uses Core Web Vitals to measure how users interact with your site. A slow, unstable, or unresponsive website leads to higher bounce rates and lower rankings.
Key Core Web Vitals Metrics:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) – This measures how long it takes for the most important content (like an image or heading) to load. If it takes longer than 2.5 seconds, your page is too slow.
- First Input Delay (FID) – This measures how quickly your site responds to a user’s first interaction (like clicking a button). A delay of over 100 milliseconds makes the site feel sluggish.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) – This tracks how much your content unexpectedly moves around while loading. If buttons and text shift as the page loads, users may click on the wrong thing, leading to frustration. A good CLS score is under 0.1.
How to Improve UX & Core Web Vitals
To provide a smooth, fast, and stable user experience, focus on:
- Speeding Up LCP – Compress images, use next-gen formats like WebP, enable browser caching, and use a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to load content faster.
- Reducing FID Delays – Defer non-essential JavaScript, optimize third-party scripts, and enable browser caching to speed up interactions.
- Fixing CLS Issues – Always set width and height for images and videos, avoid dynamically inserting elements above existing content, and ensure ads or pop-ups don’t push important content down the page.
Run a Google PageSpeed Insights test to measure Core Web Vitals and find specific areas for improvement. Apply optimizations like image compression, lazy loading, minifying CSS/JavaScript, and reducing render-blocking resources. A well-optimized UX is a crucial part of any on-page SEO audit checklist, helping both beginners and experienced SEOs achieve better rankings and engagement.
Step #5: Ensure Mobile-Friendliness & Proper Indexing
With Google’s mobile-first indexing, your website’s mobile version is the primary version that Google crawls and ranks. If your site isn’t fully optimized for mobile, it could lead to indexing issues, poor rankings, and a frustrating user experience. Ensuring mobile compatibility is a critical step in any on-page SEO audit checklist.
To give you more idea, here are the key factors for mobile-friendliness & indexing
- Mobile-Friendly Design – A responsive design automatically adjusts to different screen sizes, ensuring a seamless experience on smartphones, tablets, and desktops. Non-responsive sites require users to zoom in and scroll sideways, which increases bounce rates.
- Proper Indexing – Pages that appear as “Discovered – currently not indexed” in Google Search Console (GSC) indicate that Google found them but hasn’t added them to its index. This can happen due to low-quality content, crawl budget issues, or technical errors.
- Viewport Configuration – A meta viewport tag ensures your page scales properly on mobile screens. Missing or incorrect tags cause improper zooming and layout issues, making content unreadable on smaller screens.
| Step | Action | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Test Mobile-Friendliness | Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test | Identifies issues like small text, cramped clickable elements, and content wider than the screen. |
| Monitor Mobile Usability | Check Google Search Console > Mobile Usability | Spots and fixes errors affecting mobile pages. |
| Ensure Responsive Design | Switch to a mobile-responsive theme or update CSS | Adjusts layouts dynamically for mobile compatibility. |
| Fix Indexing Issues | Use GSC > Coverage Report to review indexing status | Addresses “Crawled – not indexed” or “Discovered – not indexed” errors; improve content, remove noindex tags, submit manually. |
| Optimize Mobile Speed | Compress images, enable lazy loading, minify CSS/JS, use a CDN | Ensures fast-loading mobile pages. |
Run a Google Mobile-Friendly Test and fix any reported issues. Use Google Search Console to check for mobile usability errors and indexing problems. Implement a responsive design, optimize mobile page speed, and ensure proper viewport settings. Keeping your site mobile-friendly is an essential step in any free on-page SEO audit checklist, improving rankings and enhancing user experience.
Step #6: Maximize Internal Links & Fix Broken Links
Internal linking is a crucial part of on-page SEO that helps search engines understand site structure, distributes link equity, and improves user navigation. A well-structured internal linking strategy enhances discoverability, while broken links create a poor user experience and can negatively impact rankings.
To optimize internal links:
- Identify orphan pages (pages with no internal links pointing to them) using Google Search Console, Screaming Frog, or Ahrefs, and add relevant links from high-authority pages.
- Use descriptive anchor text instead of generic terms like “click here.” A better example would be “check out our on-page SEO checklist for website optimization.”
- Ensure a logical linking structure, connecting important pages (such as service pages, high-converting blog posts, and category pages) to improve crawlability and user experience.
Broken links hurt both SEO and user experience. They occur when a linked page is removed or the URL structure changes without a proper redirect. To fix them:
- Find broken links using Google Search Console, Screaming Frog, or Ahrefs.
- Redirect with 301s if a broken page has a relevant replacement, ensuring users and search engines reach the correct content.
- Update or remove dead links if there’s no suitable replacement.
- Check external links and either replace broken ones with updated sources or remove them entirely.
If there are errors, use on-page SEO audit for beginners tools like Google Search Console to identify orphan pages and broken links. Implement an on-page SEO audit template to create a structured internal linking strategy. Ensure all key pages are properly linked, and fix broken links with 301 redirects or replacements.
Step #7: Conduct a Backlink & Competitor Audit
Off-page SEO plays a significant role in rankings, and a backlink audit helps ensure your site has a strong, high-quality link profile. Weak or toxic backlinks can harm your SEO, while strategic competitor analysis can reveal new link-building opportunities.
To conduct an effective backlink audit:
- Identify toxic backlinks that could trigger Google penalties, such as spammy, low-quality, or irrelevant links.
- Find lost or broken backlinks that previously pointed to your site but are now inactive or removed. Reclaiming these links can help restore lost SEO value.
- Analyze competitor backlinks to discover websites linking to them but not to you. These are potential outreach opportunities for guest posts, partnerships, or content promotion.
Use Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Moz to audit your backlink profile. If you identify toxic backlinks, submit a disavow file in Google Search Console to prevent them from impacting your rankings.
Step #8: Optimize for Featured Snippets & Search Intent
Google’s Featured Snippets appear at the top of search results, often referred to as “Position Zero.” They provide quick, direct answers to user queries and significantly boost click-through rates (CTR) and organic traffic. Optimizing for Featured Snippets increases your chances of outranking competitors and securing more visibility in SERPs (Search Engine Results Pages).
To improve your chances of ranking for Featured Snippets:
| Aspect | Action | Details & Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Target Question-Based Keywords | Focus on searches like “How to do an on-page SEO audit” or “What is an on-page SEO checklist?” | Use Google Search Console or SEO tools to identify relevant user queries. |
| Use Clear Formatting | Structure content with bullet points, numbered lists, or tables | – Numbered list: “How to do an on-page SEO audit” (step-by-step guide) – Table: Comparison of SEO tools |
| Match Search Intent | Align content with user needs based on intent type | – Informational: Guides, FAQs – Detailed explanations – Transactional: Product pages – Clear CTAs – Navigational: Brand searches – Optimized structure & links |
Be sure to update existing content to include well-structured answers using bullet points, step-by-step guides, or concise definitions. Run an on-page SEO audit for beginners to identify pages that can be optimized for Featured Snippets.
Use onpageSEO.ai to track keyword distribution, density, and optimization for ranking in featured snippets. Learn more about Technical SEO vs. Content SEO and how to optimize each for better search visibility.
Step #9: Audit Your Structured Data & HTTPS Implementation
Structured data (Schema markup) is a powerful SEO tool that helps search engines understand your content better and enhances the way your pages appear in search results. By properly implementing structured data, you increase the chances of appearing in rich results (also called rich snippets), which can include elements like star ratings, FAQs, product details, and event information. These visually enhanced search results can improve click-through rates (CTR) and drive more organic traffic to your website.
To ensure your structured data is optimized for search engines:
- Apply Schema Markup Correctly – Apply schema markup to key content types (articles, products, FAQs, and reviews).
- Validate Your Structured Data – Errors in schema markup can prevent Google from displaying rich results. Use Google’s Rich Results Test to check for issues and validate your structured data. If any warnings or errors appear, fix them in your JSON-LD, Microdata, or RDFa markup.
- Check HTTPS Security – Google prioritizes secure websites, and an unsecured site with HTTP instead of HTTPS can trigger “Not Secure” warnings in browsers. This can negatively impact trust and rankings. Verify that your SSL certificate is active and that all site pages are properly redirected to HTTPS.
Run an on-page SEO audit checklist to verify that structured data is applied to all critical pages. Use Google Search Console to monitor schema markup issues and fix validation errors. Additionally, perform a site-wide HTTPS check to ensure every page is secure and properly redirected from HTTP to HTTPS.
Step #10: Set Up Rank Tracking & Monitor Performance
Tracking your SEO progress is essential to measure improvements and identify new opportunities. Regular monitoring helps you stay ahead of algorithm changes and competitors.
- Use Google Search Console & Google Analytics to track keyword rankings, traffic trends, and technical fixes.
- Set up Google Looker Studio (formerly Data Studio) for a custom SEO dashboard that consolidates data from multiple sources.
- Monitor competitor rankings to identify keyword gaps and new opportunities.
Set up automated rank tracking with tools like SEMrush, Ahrefs, or AccuRanker to monitor keyword movements and SEO performance over time. Regular tracking ensures your on-page SEO strategy stays effective.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How to do an on-page SEO audit?
An on-page SEO audit involves analyzing organic traffic, meta tags, keyword optimization, internal links, UX, and technical factors like Core Web Vitals and mobile-friendliness. Use tools like Google Search Console, Screaming Frog, and Ahrefs for insights.
How to audit off-page SEO?
An off-page SEO audit focuses on backlink analysis, brand mentions, social signals, and competitor strategies. Tools like Ahrefs and SEMrush can help track toxic backlinks and find link-building opportunities.
What is included in on-page SEO?
On-page SEO includes content optimization, title tags, meta descriptions, internal linking, mobile-friendliness, page speed, structured data, and Core Web Vitals. These elements help improve rankings and user experience.
Final Thoughts
A well-executed on-page SEO audit is key to improving your website’s rankings, user experience, and overall performance. By following this checklist, you can identify and fix critical issues that may be holding your site back. From optimizing on-page elements to improving site speed and mobile-friendliness, every step helps boost your visibility in search results.
Ready to optimise your website effortlessly? Try OnPageSEO.ai for AI-powered audits and instant recommendations. Get started today!



